
Clot Retraction Time Test For Blood Clotting
The Clot Retraction Time Test assesses how long it takes for a blood clot to change from a liquid to a more solid state, helping to evaluate the blood's ability to clot properly.
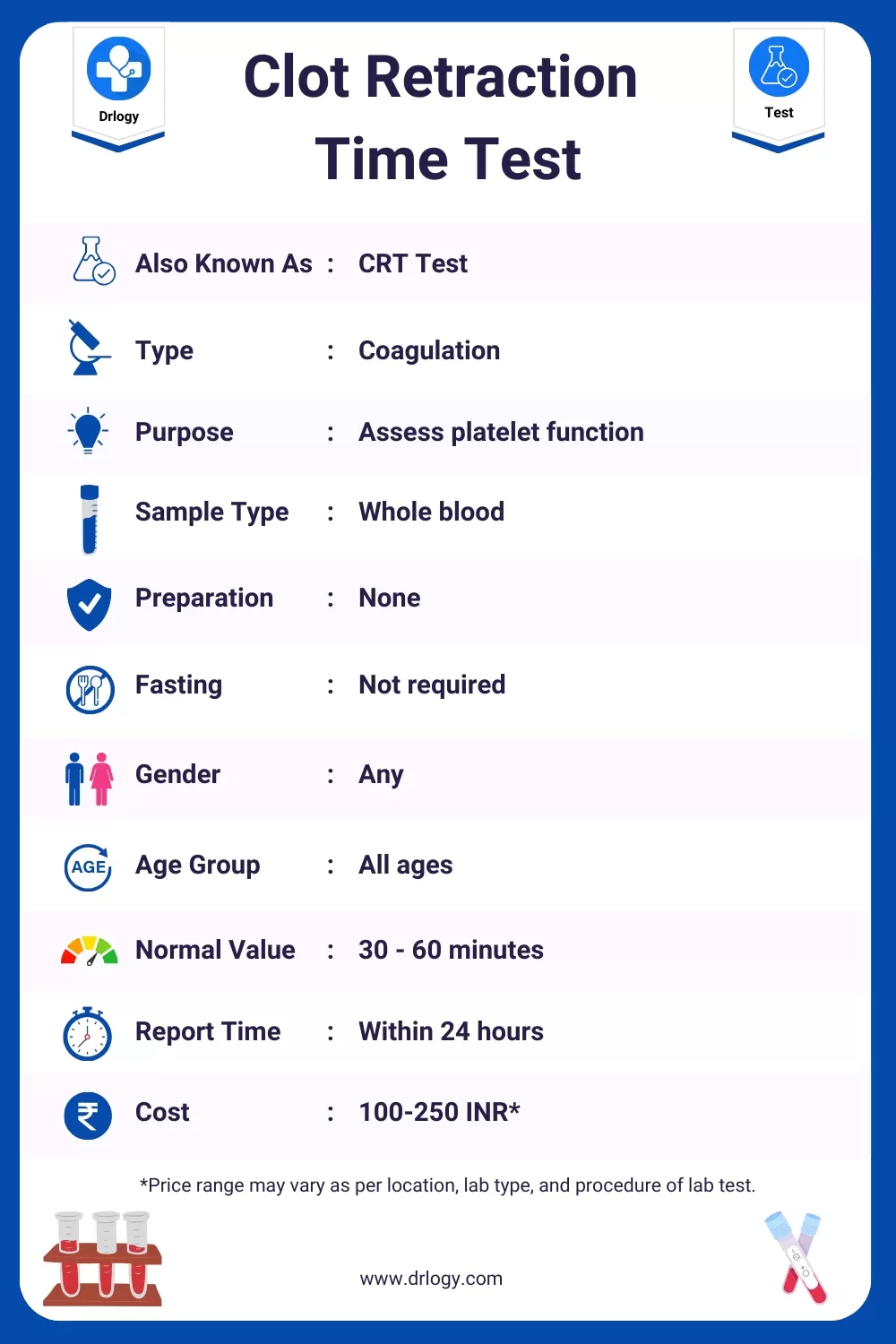
Clot Retraction Time Test
Here are the basic details of the Clot Retraction Time Test.
| Test Name | Clot Retraction Time Test |
|---|---|
| Also Known As | CRT Test |
| Type | Coagulation |
| Purpose | Assess platelet function |
| Sample Type | Whole blood |
| Preparation | None |
| Fasting | Not required |
| Gender | Any |
| Age Group | All ages |
| Normal Value | 30 - 60 minutes |
| Reporting Time | Within 24 hours |
| Cost | 100-250 INR* |
*Clot Retraction Time Test Price range may vary as per location, lab type, and lab test procedure.
Clot Retraction Time Test Means
The clot retraction time test is a laboratory examination used to assess the efficiency of blood clot formation and retraction.
- It measures the time it takes for a blood clot to contract and become denser after it initially forms.
- This test is crucial in evaluating the overall functioning of platelets and the clotting process.
- Abnormal clot retraction times may indicate disorders like thrombocytopenia or impaired platelet function.
- It's an essential diagnostic tool in the investigation of bleeding disorders and hemostasis abnormalities.
- Results from this test help healthcare professionals understand the patient's clotting ability and guide appropriate treatmen
Clot Retraction Time Test Purpose
The purpose of the Clot Retraction Time Test is to:
- Evaluates the efficiency of blood clot formation.
- Assesses the ability of blood clots to contract and become denser.
- Aids in diagnosing and monitoring bleeding disorders.
- Guides treatment decisions for patients with clotting abnormalities.
- Provides insights into overall hemostasis and platelet function.
Clot Retraction Time Test Preparation
Here is the basic preparation for the Clot Retraction Time Test.
Before Test
- Follow any pre-test instructions provided by your healthcare provider, such as fasting or discontinuing specific medications.
- Inform the healthcare team about any medical conditions, medications, or allergies that may be relevant to the test.
- Ask any questions you have about the procedure to ensure you fully understand what will happen.
During Test
- Stay calm and cooperative during the blood sample collection, as this will help ensure a successful procedure.
- Inform the phlebotomist or healthcare provider if you experience any discomfort or anxiety during the venipuncture.
- Be patient and wait for the healthcare provider to complete the test while following their instructions.
After Test
- Relax and allow the healthcare team to observe the clot retraction time without interference.
- Inquire about when you can expect to receive the test results and any potential follow-up steps.
- Continue with your normal activities, unless advised otherwise by the healthcare provider
Clot Retraction Time Test Procedure
Here is the basic Clot Retraction Time Test Procedure.
- Obtain a blood sample from the patient via venipuncture.
- Place the blood into a test tube and allow it to clot for a specified period.
- After clot formation, carefully tilt the tube to observe clot retraction.
- Record the time it takes for the clot to contract and retract.
- Compare the results to established reference ranges.
- Abnormal clot retraction times may necessitate further diagnostic tests.
Clot Retraction Time Test Result
Here is the basic reading of the Clot Retraction Time Test results.
- Clot Retraction Time (CRT) test results are evaluated in minutes and represent the time it takes for a blood clot to contract and become denser after initial formation.
- Normal CRT values typically fall within a specific range (e.g., 30-60 minutes), indicating effective clot formation and retraction.
- Prolonged CRT may suggest impaired platelet function or disorders affecting the clot retraction process.
- Shortened CRT times are less common but may occur in specific conditions, often associated with hypercoagulable states or factors influencing clot stability.
Clot Retraction Time Test Normal Result Report

Clot Retraction Time Test Normal Report
Clot Retraction Time Test Abnormal Result Report

Clot Retraction Time Test Abormal Report
Clot Retraction Time Test Normal Range
Here is the normal range of the Clot Retraction Time Test.
| Age Group | Normal Range for CRT (minutes) |
|---|---|
| Adults | 30 - 60 minutes |
| Children | 30 - 60 minutes |
Clot Retraction Time Test Interpretation
Here is the Interpretation of the Clot Retraction Time Test.
| CRT Test Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| < 30 minutes | Faster than normal clot retraction time. Possible hypercoagulability or clotting disorder. |
| 30 - 60 minutes | Within the normal range. |
| > 60 minutes | Slower than normal clot retraction time. May suggest a clotting factor deficiency or platelet dysfunction. |
High Clot Retraction Time
Here are the potential causes of high Clot Retraction Time Test levels:
| Potential Causes | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Clotting Factor Deficiency | Deficiency in clotting factors, such as hemophilia. |
| Platelet Dysfunction | Impaired platelet function can delay clot retraction. |
| Liver Disease | Liver dysfunction can lead to decreased clotting factors. |
| Anticoagulant Medications | Medications that interfere with clot formation. |
| Blood Disorders (e.g., Thrombocytopenia) | Conditions causing low platelet counts. |
| Vitamin K Deficiency | Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting. |
Low Clot Retraction Time
Here are the potential causes of low Clot Retraction Time Test levels:
| Potential Causes | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Hypercoagulability | Excessive blood clotting, as seen in thrombosis. |
| Elevated Clotting Factors | Increased levels of clotting factors. |
| Acquired Clotting Disorders | Conditions like disseminated intravascular coagulation. |
| Inflammation or Infection | These conditions can lead to a pro-coagulant state. |
| Blood Disorders (e.g., Polycythemia) | Conditions causing high red blood cell counts. |
| Medications (e.g., Oral Contraceptives) | Some medications can increase clotting risk. |
Specimen Requirements For Clot Retraction Time Test
Here are the specimen requirements for the Clot Retraction Time Test.
| Specimen | Blood Plasma | |
| Volume | 1 mL | |
| Container | Na Cit | |
| Collection | Plasma Na Cit | |
| Storage | Room temperature | |
| Sample Stability | Temperature | Period |
| Frozen | 14 days | |
| Causes for Rejection | Gross hemolysis, Gross lipemia, and Gross icterus | |
Clot Retraction Time Test is Safe?
The Clot Retraction Time Test is generally safe and minimally invasive.
- It involves a routine blood sample collection, similar to a standard blood draw.
- Risks are typically limited to those associated with venipuncture, such as minor bruising or discomfort at the site.
When Do You Get Clot Retraction Time Test Results?
- Clot Retraction Time Test results are typically available within 24 hrs, depending on the laboratory's testing schedule.
- Patients should consult their healthcare provider or the testing facility for specific information regarding result turnaround times.
Clot Retraction Time Test Limitation
Here is the basic limitation of the Clot Retraction Time Test.
- Limited clinical utility, as it is not routinely used for diagnosing bleeding disorders.
- Cannotentify the specific clotting factor deficiencies or abnormalities.
- Results can be affected by external factors such as temperature and handling.
- Replaced by more sensitive and specific tests like the prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT).
- Not suitable for assessing bleeding risk in many clinical scenarios.
Clot Retraction Time Test Risk Factors
Here are some of the risk factors of the Clot Retraction Time Test.
- Not typically associated with specific risk factors, as it's not a common diagnostic test.
- May be influenced by variations in the patient's clotting system, but these factors are not well-defined for this test.
- Test results may be affected by pre-analytical factors like sample handling and temperature.
- Lack of standardized reference ranges can make interpretation challenging.
- Generally, the risk factors for clotting disorders are assessed using other, more specific tests.
Doctor Recommendations After Clot Retraction Time Test Result
Here are the Doctor's recommendations or consult a specialist after the Clot Retraction Time Test.
| CRT Result | Doctor to Visit | Reason for Visit |
|---|---|---|
| High | Hematologist | Clotting issues or disorders |
| Normal | General Doctor | Routine assessment |
| Low | Hematologist | Possible hypercoagulability |
Clot Retraction Time Test Price
Here are the estimated Clot Retraction Time Test Prices in India with different top cities:
| City | Price Range (INR)* |
| 100-250 | |
| 150-250 | |
| 100-250 | |
| 150-250 | |
| 100-250 | |
| 150-250 | |
| 100-250 | |
| 150-250 | |
| 150-250 | |
| 100-250 | |
| 150-250 | |
| 100-250 | |
| 150-250 | |
| 100-250 |
*Clot Retraction Time Test Price are approximate and vary depending on a specific laboratory or healthcare facility.
Summary
Overall, Clot Retraction Time Test is contributed of clotting processes, paving the way for more sophisticated and precise coagulation tests. Also check Drlogy Test for detailed information about all medical tests for patients, doctors, scholers and medical students.
Reference




